
1800s Plasters to Induce Blisters, courtesy Library of Virginia
For much of psychiatry’s history, experts were only able to treat symptoms, rather than the causes of mental illness. When insane asylums first came into public use, most alienists had largely abandoned Dr. Benjamin Rush’s (considered the Father of American Psychiatry) depleting treatments, but they still had to find ways to deal with their patients’ moods and behaviors.
One treatment popular in this beginning era of psychiatry was to use a counter-irritant on patients. Doctors would blister someone who was manic in order to divert his/her attention; they would also blister someone who was melancholic in order to “divert the mind from its morbid train of thought.”

Tartar Emetic Was Definitely Potent
For recent cases of insanity–also called acute cases and the most hopeful of recovery–alienists applied tartar emetic ointment to the back of the neck. This ointment consisted of potassio-tartrate of antimony added to one ounce of lard or other carrier; the compound “will produce an eruption on the skin very similar to small-pox in appearance.” Presumably the pain of the treatment would keep a patient’s mind off his original problem. Cold compresses to the head, cold baths or showers, and warm baths with vigorous rubbing of the extremities were also useful treatments for insanity.
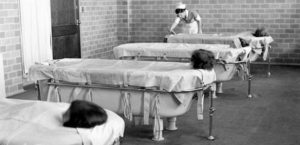
Water Therapy Could be as Confining as Restraints
Readers will note that all these treatments were uncomfortable if not actually painful for the patients. However, inflicting pain seldom deterred alienists intent on “helping” their patients with mental issues.
(These treatments are discussed by Dr. Edward Cowles in the July, 1894 issue of the American Journal of Insanity in his review of psychiatry’s progress over the past few decades.)